Training structure
Faculty of Science
Program
Fluorinated and phosphorous biomolecules: synthesis and applications
2 creditsOPTION 1
4 creditsChoose 2 out of 3
Solutions, colloids, interfaces
2 creditsSeparation techniques
2 creditsAnalysis of volatile molecules
2 credits
Polymers for health
2 creditsHeterocyclic chemistry
2 creditsChemistry of natural products
2 creditsLiquid NMR spectroscopy and X-ray diffraction
2 creditsAnalysis of biomolecules by mass spectrometry
2 creditsChemometrics, statistical data analysis, experimental design
2 creditsOrganometallic chemistry and heteroelement chemistry
2 creditsCoordination chemistry and organic chemistry
2 creditsProfessional projects – project monitoring
8 credits
2-4 month M1 internship with thesis defense/report in English
10 creditsNucleosides and derivatives
2 creditsInnovative synthesis and extraction processes
2 creditsMedicinal chemistry
2 creditsAsymmetric synthesis
2 creditsAmino acids and derivatives
2 creditsBio-based chemistry
2 creditsCommunication and professional integration
2 creditsOPTION 2
4 creditsChoose 2 out of 3
Introduction to modeling
2 creditsHybrid and structured materials
2 creditsNanomaterials
2 credits
Strategy and tools in organic synthesis
2 credits
Fluorinated and phosphorous biomolecules: synthesis and applications
Level of education
Bachelor's degree
ECTS
2 credits
Training structure
Faculty of Science
Fluorinated biomolecules. Current developments in fluorinated molecules. Fluorination methods: nucleophilic and electrophilic monofluorination, introduction of difluoromethyl or trifluoromethyl groups. Contribution of fluorine atoms to the activity of these compounds. Examples of syntheses of fluorinated compounds used as antitumor agents, antivirals, antidepressants, anxiolytics, anti-inflammatories, etc.
Phosphorus-containing biomolecules. Structure, nomenclature, reactivity, structural analysis, and applications.
Several methods for synthesizing compounds from each of the families covered will be discussed, highlighting unconventional activation methods where applicable. Biomedical applications will be targeted, as well as other applications in agrochemistry, optoelectronics, nanomaterials, etc.
Hourly volumes:
CM: 15 hours (7.5 hours fluorinated biomolecules and 7.5 hours phosphorous biomolecules)
Tutorial: 5 hours
Solutions, colloids, interfaces
Level of education
Bachelor's degree
ECTS
2 credits
Training structure
Faculty of Science
This course unit enables students to acquire basic knowledge and cross-disciplinary skills in the field of colloids and interfaces, which are common to the various tracks of the Master's degree in Chemistry (Materials Chemistry, Separative Chemistry, Materials and Processes, ICAP Cosmetics Engineering, Biomolecular Chemistry). It is also offered to international students enrolled in the SFRI program at the University of Montpellier, where courses are taught in English. An introductory presentation on basic notions and concepts will enable students to discover and better understand the main physicochemical properties of colloidal dispersions, associative colloids, and macromolecular solutions, as well as the parameters and phenomena governing stability in colloidal dispersions and mixed solution-colloid systems. This will be followed by interdisciplinary practical teaching based on the flipped classroom principle to help students build and deepen their knowledge through individual and collective analysis of the various applications of colloidal and interfacial phenomena and systems.
Hourly volumes:
CM: 7
TD: 13
Separation techniques
Level of education
Bachelor's degree
ECTS
2 credits
Training structure
Faculty of Science
This course aims to teach liquid chromatography and gas chromatography.
Hourly volumes:
CM: 3:00 p.m.
Tutorial: 5 hours
Analysis of volatile molecules
Level of education
Bachelor's degree
ECTS
2 credits
Training structure
Faculty of Science
Knowledge of gas chromatography techniques and mass spectrometry with electron impact ionization and quadrupole mass analyzer for the analysis of volatile organic molecules.
1) GC-MS analyses of volatile organic compounds:
- Electron impact (EI) ionization techniques
- Chemical ionization (CI) techniques
- Quadrupole (Q) analysis techniques
- GC/MS Couplings
2) Applications in organic chemistry analysis and characterization of volatile samples.
Hourly volumes*:
CM: 3 p.m.
Tutorial: 5 hours
Polymers for health
Level of education
Master's degree
ECTS
2 credits
Training structure
Faculty of Science
Knowledge of the major families of polymers used in the biomedical field.
1) Specificity of polymers for biomedical applications and major families of polymers used
2) Description of application families
3) Discussion on the concept of synthesis and the relationship between structure, properties, and specifications
Hourly volumes*:
CM: 3 p.m.
Tutorial: 5 hours
Heterocyclic chemistry
Level of education
Bachelor's degree
ECTS
2 credits
Training structure
Faculty of Science
This course concisely and systematically covers all aspects of heterocyclic chemistry, from nomenclature to applications such as the principles of action of medicines, toxins, drugs, pigments, food colorings, etc.
Hourly volumes*:
CM: 3 p.m.
Tutorial: 5 hours
Chemistry of natural products
Level of education
Bachelor's degree
ECTS
2 credits
Training structure
Faculty of Science
Natural products occupy a major place in the field of biomolecular chemistry. They represent an important source of bioactive compounds for medicinal chemistry. This teaching unit provides a comprehensive overview of secondary metabolism and the origin of natural products derived from plants. This teaching unit will focus on the organic chemistry behind the various biotransformations that occur during the biosynthesis of each major class of molecule. A mechanistic approach will be used to understand the chemical basis of each transformation.
Hourly volumes*:
CM: 13
TD: 7
Liquid NMR spectroscopy and X-ray diffraction
Level of education
Bachelor's degree
ECTS
2 credits
Training structure
Faculty of Science
NMR:
Liquid-phase NMR (Nuclear Magnetic Resonance) is an essential spectroscopic analysis method for chemists, enabling them to determine the structure of small organic molecules or macromolecules in solution, study dynamic phenomena, and more. The aim of this course unit is to understand the phenomena involved in this technique and to relate them to the various structural information accessible by this method. The goal is to be able to use the spectral data from this analysis to elucidate the structure and stereochemistry of organic molecules or polymer structures, or to monitor reactions.
X-ray diffraction:
X-ray diffraction is a powerful, non-destructive technique for characterizing the crystalline structure of materials. It can also provide crystallographic and structural information such as lattice parameters and atomic positions. This includes all crystallized materials such as ceramics, materials for energy and information storage and conversion, as well as organic molecules and metal complexes (interatomic distances and angles, stereochemistry (chirality, stereoisomerism, etc.), intra- and intermolecular bonds, etc.). The objective of this course unit is to provide an introduction to crystallography and diffraction, with the aim of understanding the operation and characteristics of an X-ray diffractometer, as well as interpreting diffraction patterns (structural analysis, lattice parameters).
Hourly volumes:
CM: 10
TD: 10
Analysis of biomolecules by mass spectrometry
Level of education
Bachelor's degree
ECTS
2 credits
Training structure
Faculty of Science
Knowledge of the latest mass spectrometry techniques for the qualitative analysis of organic molecules and biomolecules.
1) Description of fundamental principles (Ion science and technology):
- Ionization techniques
- Analysis techniques
- Tandem mass spectrometry (MS/MS)
- LC/MS and LC/MS/MS couplings
2) Application in the context of biomolecule analysis and monitoring of organic chemistry reactions.
Hourly volumes*:
CM: 3 p.m.
Tutorial: 5 hours
Chemometrics, statistical data analysis, experimental design
Level of education
Bachelor's degree
ECTS
2 credits
Training structure
Faculty of Science
This course will cover the fundamental concepts and practical tools related to chemometrics through: - statistical data analysis;
- the laws of probability;
- confidence interval estimation;
- parametric and nonparametric tests.
An introduction to design of experiments will be offered at the end of the module.
Hourly volumes:
CM: 7 a.m.
TD: 1:00 PM
Organometallic chemistry and heteroelement chemistry
Level of education
Bachelor's degree
ECTS
2 credits
Training structure
Faculty of Science
The first part of the course presents the fundamental knowledge of organometallic chemistry of transition metals. It begins with a description of the metal-carbon bond, enabling an understanding of its stability and chemical reactivity. Next, we will demonstrate the power of this synthesis tool for forming C-H, C-C, and other bonds. Examples of their applications in different fields will help students learn about these reactions and their fields of application: fine chemistry, catalytic transformations of industrial importance, synthesis of natural products, and preparation of materials.
The second part of this course is devoted to the chemistry of heteroelements, focusing on silicon, tin, and boron. This part aims to present the different methods of preparing boron-, tin-, and silicon-based reagents, as well as the main transformations carried out with these compounds, with applications in organic synthesis and materials synthesis.
CM: 1:00 PM
Tutorial: 7 hours
Coordination chemistry and organic chemistry
Level of education
Bachelor's degree
ECTS
2 credits
Training structure
Faculty of Science
This teaching unit is dedicated to deepening the foundations of organic chemistry and coordination chemistry covered in L3 and to acquiring concepts related to molecular engineering and molecular chemistry. The teaching unit consists of lectures and tutorials. Students will prepare for certain lectures and tutorials using course materials provided, enabling them to participate fully in the lectures and tutorials, understand the concepts presented, and acquire the necessary skills. The progression program and activities will be proposed. For students who have not studied the basics of coordination chemistry and organic chemistry, documents will be made available.
Coordination chemistry: The course will cover various aspects of transition metal and lanthanide complexes, molecular materials (polynuclear complexes and coordination polymers with extended structures (MOFs, etc.)) as well as their properties and applications. Structural aspects, bond descriptions, properties, and aspects related to stability and reactivity will be addressed. Emphasis will be placed on the complexation effect and the stability of metal, lanthanide, and actinide complexes with certain ligands for applications in the biomedical field (imaging and therapy), decontamination (nuclear field), etc. The electronic (relaxivity, magnetism) and optical (absorption, luminescence) properties of these complexes will be discussed and placed in the context of applications in various fields, such as imaging, electronics, sensors, etc.
Organic Chemistry: The course builds on the knowledge acquired in the Bachelor's degree and will use a reasoned study approach to address the main reaction mechanisms in organic chemistry, providing a common foundation for all students in the Master's in Chemistry program. The main processes (substitution, addition, elimination, transposition, etc.) and their essential characteristics and applications to mechanistic sequences will be examined. This course should provide students with general tools for analyzing mechanisms (ionic, radical, concerted) in order to understand these mechanisms in all their variety.
Hourly volumes:
CM: 1:00 PM
Tutorial: 7 hours
Professional projects – project monitoring
Level of education
Bachelor's degree
ECTS
8 credits
Training structure
Faculty of Science
The professional project bridges the gap between traditional practical work and internships in laboratories or companies. It takes the form of a supervised project consisting of placing students in a professional situation through collaborative (group) work based on carrying out a project in response to a problem set by a company, local authority, association, or academic. It is part of the core curriculum of the Master's in Chemistry and is carried out under the supervision of a member of the teaching team (academic or industrial). Conducted throughout the semester, this project aims to connect and consolidate the knowledge and skills acquired during the Bachelor's and early Master's programs through this professional situation. These scenarios will be directly related to the Master's program chosen by the students. In addition to chemistry-specific skills, other interpersonal, organizational, and communication skills intrinsically linked to project management will also be acquired, equipping students for their future professional lives.
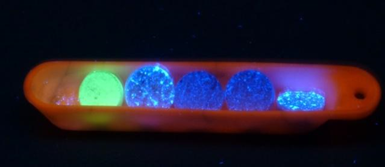
Addressing a research issue: example of a summary of new phosphorescent materials.
Hourly volumes:
CM: 5 hours
Tutorial: 5 hours
Practical work: 40 hours
2-4 month M1 internship with thesis defense/report in English
Level of education
Bachelor's degree
ECTS
10 credits
Training structure
Faculty of Science
The internship in semester 8 of the Master 1 in Biomolecular Chemistry aims to familiarize students with careers in life sciences research. Students will have the opportunity to complete this introductory research internship in academic or private laboratories. Subject to prior approval by the teaching team (internship topic related to the Master's program and appropriate environment/resources), students may seek a host team in an academic setting at one of the institutes of the Chemistry Cluster at the University of Montpellier (IBMM, ICGM, , etc.), in academic laboratories outside the University of Montpellier (in France or abroad), or in the private sector (chemical, pharmaceutical, and agri-food industries, biotechnology laboratories, etc.).
Fieldwork: 2 to 4 months of internship
Nucleosides and derivatives
Level of education
Bachelor's degree
ECTS
2 credits
Training structure
Faculty of Science
Nucleosides are the basic building blocks of nucleic acids (DNA and RNA). As such, they play an essential role in many biological processes. This course will present the structure and biological role of natural nucleosides. The main methods of synthesis and characterization of these compounds and their analogues (glycosylation reactions, structural modifications of the furanose ring, substitution and introduction of heteroatoms, configuration inversion, etc.) will also be discussed. The use of nucleoside analogues for the treatment of viral diseases and cancers will also be addressed.
Hourly volumes:
CM: 3 p.m.
Tutorial: 5 hours
Innovative synthesis and extraction processes
Level of education
Bachelor's degree
ECTS
2 credits
Training structure
Faculty of Science
This teaching unit is shared by MI students in the Master's in Chemistry program: ICAP P1, ICAP P2, MAT P1, MAT P2, and BM (semester S2) courses. The following topics will be covered:
- The 12 Principles of Green Chemistry and units of measurement in Green Chemistry;
- Synthesis strategies in sustainable chemistry;
- Alternative or eco-friendly solvents for synthesis and extraction;
- Unconventional activation techniques and applications.
CM: 13
Tutorial: 7 hours
Medicinal chemistry
Level of education
Bachelor's degree
ECTS
2 credits
Training structure
Faculty of Science
The aim of teaching medicinal chemistry is to introduce students to the key stages in the process of developing molecules with biological activities. In particular, a description of the interactions involved, the concept of pharmacophores, bioisosterism, etc., as well as structure-activity relationship studies will be covered, enabling students to consider appropriate strategies and structural modifications.
Hourly volumes:
CM: 3 p.m.
Tutorial: 5 hours
Asymmetric synthesis
Level of education
Bachelor's degree
ECTS
2 credits
Training structure
Faculty of Science
After covering the basics of prochirality and stereochemistry, this course will introduce the tools needed to master diastereoselective and enantioselective synthesis. The various approaches will be presented in a detailed and rational manner. Examples of industrial synthesis of chiral bioactive molecules will be discussed.
Hourly volumes*:
CM: 3 p.m.
Tutorial: 5 hours
Amino acids and derivatives
Level of education
Bachelor's degree
ECTS
2 credits
Training structure
Faculty of Science
This course covers synthesis methods applied to obtaining enantiopure amino acids, as well as the use of chiral amino acids for the synthesis of other enantiopure compounds.
These amino acids are the basic building blocks of peptides. The different physicochemical properties induced by the nature of these amino acids will enable the definition of strategies for synthesizing peptides of interest and their characterization.
Hourly volumes*:
CM: 3 p.m.
Tutorial: 5 hours
Bio-based chemistry
Level of education
Bachelor's degree
ECTS
2 credits
Training structure
Faculty of Science
The following topics will be covered:
- Bio-based solvents
- Fuels derived from biomass
- Antioxidants derived from lignin
- Metal catalysts derived from plants
- Surfactants obtained from renewable resources
- Examples of industrial applications of enzymatic synthesis
Hourly volumes*:
CM: 15
TD: 5
Communication and professional integration
Level of education
Bachelor's degree
ECTS
2 credits
Training structure
Faculty of Science
This EU will address, in small groups or on an individual basis, teaching tools and best practices related to communication and professional integration, through:
- assessment of knowledge, skills, competencies, interpersonal skills, and motivations;
- awareness of job search techniques;
- writing resumes and cover letters;
- rules for oral and written communication;
- job interview simulations.
Scenarios directly related to the sectors of activity targeted by the courses of the students concerned will be offered.
Practical work: 20 hours
Introduction to modeling
Level of education
Bachelor's degree
ECTS
2 credits
Training structure
Faculty of Science
General overview of the most commonly used calculation and modeling methods in the field of solid-state chemistry according to the spatial and temporal scales that can be studied with them:
(1) Quantum calculations (Hartree Fock, Post-Hartree Fock methods, DFT),
(2) Force field-based modeling (atomistic and coarse-grained),
(3) Hybrid QMMM and AACG modeling.
Presentation of different calculation techniques: static and optimization calculations, molecular dynamics, and Monte Carlo.
The EU will offer lectures and practical classes. Two practical modeling assignments will be offered: modeling techniques in classical mechanics and quantum calculations.
CM: 11 a.m.
TD: 9 a.m.
Hybrid and structured materials
Level of education
Bachelor's degree
ECTS
2 credits
Training structure
Faculty of Science
Hybrid materials are a new family of materials combining organic ligands that connect inorganic entities, and are increasingly being studied at both a fundamental and applied level.
As part of this course unit, two main categories of hybrid materials will be covered:
- Coordination Networks and Metal-Organic Frameworks
- Organosilicon/carbon materials
CM: 10 a.m.
Tutorial: 10 a.m.
Nanomaterials
Level of education
Bachelor's degree
ECTS
2 credits
Training structure
Faculty of Science
This teaching unit is dedicated to the presentation of inorganic materials and nanomaterials intended for use in the biomedical field (imaging, therapy, implants). This teaching unit builds on the knowledge acquired in teaching unit HAC930C (Development of Materials for Health). It aims to develop health issues and inorganic materials and nanomaterials in diagnosis, therapy, and well-being. Strategies for developing the inorganic materials and nanomaterials of the future based on theranostics and multifunctionality, as well as smart materials, will also be addressed.
The EU includes lectures and tutorials. Students will be offered a group project on the (theoretical) study of inorganic materials or nanomaterials for health.
CM: 11
TD: 9
Strategy and tools in organic synthesis
Level of education
Bachelor's degree
ECTS
2 credits
Training structure
Faculty of Science
The teaching of the module on strategies and tools in organic synthesis focuses on deepening students' understanding of strategies for developing molecules, whether derived from the natural environment or not, using the tools of organic chemistry.
Hourly volumes:
CM: 3 p.m.
Tutorial: 5 hours
Admission
Registration procedures
Applications can be submitted on the following platforms:
- French and European students: follow the "Mon Master" procedure on the website:https://www.monmaster.gouv.fr/
- International students from outside the EU: follow the "Études en France" procedure:https://pastel.diplomatie.gouv.fr/etudesenfrance/dyn/public/authentification/login.html


