Training structure
Faculty of Science
Program
Crystallography I
2 creditsThermodynamics and defects of solids M1
5 creditsInorganic materials
Surface properties M1
3 creditsCrystallography II and Electron Microscopy
6 creditsThin films and extreme conditions M1
3 creditsMaterials for catalysis M1
3 creditsQuantum Mechanics and Modeling I
5 credits
Metallurgy and electronics properties
5 creditsResearch internship
10 creditsProject internship
3 creditsQuantum Mechanics and Modeling II
7 creditsCrystallography, crystal chemistry, large-scale facilities
5 credits
Crystallography I
Level of education
Bachelor's degree
ECTS
2 credits
Training structure
Faculty of Science
This lecture, delivered entirely in English, provides a basic introduction to crystallography and electron diffraction for beginners. X-ray diffraction is an important characterization technique in modern chemistry; the majority of crystalline structures in inorganic and organic solids have been solved using this method. It is therefore important for all students to understand its basic concepts and instrumentation. The course provides explanations and principles of X-ray diffraction together with the geometry and symmetry of X-ray patterns. In addition to the interaction principles of X-rays and matter, it covers how to obtain quantitative intensities for single crystal and powder diffraction patterns. It naturally includes an understanding of lattice planes and the reciprocal lattice concept together with the Ewald sphere construction. Furthermore, it provides a basic understanding of the Fourier transform relationship between the crystalline structure and the diffracted intensities, as well as the reciprocal lattice concept.
Electron diffraction is a complementary technique to X-rays that provides information in terms of symmetry and geometry on the materials studied. In this course, we will therefore approach the description of the method for obtaining electron diffraction patterns and their interpretation. We will be able to obtain the lattice parameters, the reflection conditions, as well as the groups of possible spaces.
This lecture also serves as the introductory part to the lecture Electron Microscopy and Crystallography II.
CM: 14
TD: 6
Thermodynamics and defects of solids M1
Level of education
Bachelor's degree
ECTS
5 credits
Training structure
Faculty of Science
This module is devoted to delivering basic knowledge on the thermodynamics of defects. Understanding the basic concepts of defects in stoichiometric and non-stoichiometric solids is an important aspect of better understanding and designing materials for ionic and electronic conductivity, with specific relevance for energy materials. The lecture introduces and discusses the nature of point defects that intrude upon the perfect geometry of ideal crystal structures:
- Introduction to point defects (missing or misplaced atoms, ions, or electrons)
- Discussion of thermodynamic concepts of order-disorder phenomena in solid solutions
- Understanding of Brouwer diagrams for oxides in order to emphasize the role of the surrounding atmosphere on defect equilibrium at high temperatures.
- Understanding of diffusion pathways and energies of ions and electrons, as a major consequence of point defects, giving rise to electrical transport is investigated for ionic conductors.
- Experimental investigations of measuring ionic conductivity versus temperature are described. The method of impedance spectroscopy measurements is discussed.
- Presentation of the Kröger-Vink Notation of defects
- Mott-Hubbard insulators
Hourly volumes:
CM: 24
TD: 12
Inorganic materials
Level of education
Bachelor's degree
Training structure
Faculty of Science
This module will be divided into 3 parts:
- General introduction: main classes of materials, relationship between properties and structure of materials
- Construction and interpretation of phase diagrams: binary (e.g., with metallic and ceramic alloys)
- Construction and interpretation of ternary phase diagrams: variance, ternary eutectic definitions, first and second order peritectic, isothermal section, study of alloy cooling.
Hourly volumes:
CM: 5 p.m.
Tutorial: 8 hours
Surface properties M1
Level of education
Bachelor's degree
ECTS
3 credits
Training structure
Faculty of Science
This course provides comprehensive knowledge and tools related to surface properties and interfacial behavior of crystalline and amorphous solids in different media. It consists of two parts: (1) Fundamentals of Colloid and Surface Science, divided and porous solids
(2) Surface characterization techniques and surface analysis
Hourly volumes:
CM: 5 p.m .
Tutorial: 8 hours
Crystallography II and Electron Microscopy
Level of education
Bachelor's degree
ECTS
6 credits
Training structure
Faculty of Science
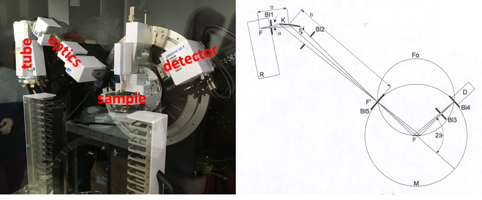
The structural characterization of materials is a mandatory prerequisite for developing functional materials and an absolute must for materials science researchers and engineers. For the interpretation of diffraction patterns, structures, microstructures, etc., detailed knowledge of crystallography, structure analysis, and the instruments used is necessary. The necessary knowledge is developed from scratch, progressively yielding an understanding of how to characterize materials by standard and sophisticated diffraction methods. The lecture also includes lab work on powder and single crystal diffractometers, allowing students to acquire the skills to correctly use and interpret diffraction data. The lecture during thefirst semester essentially covers X-ray diffraction and electron microscopy, while the crystallography part continues during thesecond semester with symmetry, structure solution, and structure refinements, as well as neutron scattering and magnetic structure analysis.
This lecture consists of two parts:
(1): Crystallography: Simple inorganic structures: basics & concepts, Fractional atomic coordinates and projections, Bravais lattices, Crystal systems, Lattice points, lines and planes, Miller indices, Zone equation, Wulff net, orienting matrix, Crystal growth and morphology, X-ray sources, interaction of X-rays, electrons and neutrons with matter, scattering lengths, structure factor, systematic extinctions, Debye-Waller factor, principles of scattering, reciprocal lattice, concept of Ewald sphere, Laue diffraction, Debye Scherrer camera, powder diffractometers, single crystal diffractometers, monochromators, detectors, resolution, stereographic projection, peak intensities, reflection profile broadening and grain size,
(2): Electron microscopy:
In this part, we will be interested in electron microscopy through flipped classes. We will discuss the following topics: Electron sources, lenses and aberrations, sample preparation, electron diffraction, structural and chemical analysis, imaging techniques.
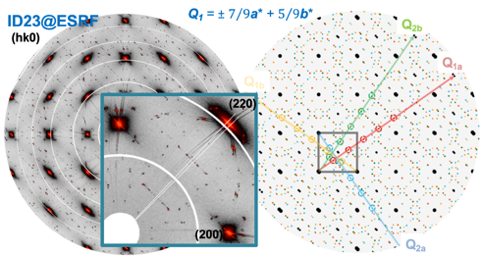
Hourly volumes:
CM: 34
TD: 18
Thin films and extreme conditions M1
Level of education
Bachelor's degree
ECTS
3 credits
Training structure
Faculty of Science
This course consists of a series of different lectures in the field of synthesis and characterization of thin films for technological applications or academic research. It is completed by an introduction into synthesis techniques of compounds stabilized under high pressure or only available under special conditions.
- Physics of Low-dimensional systems
- Quantum confinement
- Quantum wells, 1D quantum wires, 0D quantum dots
- Electron confinement and Density of States (DoS) formalism
- Epitaxial films
- Microstructure
- Dislocations and grain boundaries
- Coatings and applications
- Diffusion barriers
- Photo optical devices
- Vacuum technology
- High-pressure synthesis
Synthesis of compounds with unusual valence and coordination states
Hourly volumes:
CM: 17
TD: 8
Materials for catalysis M1
Level of education
Bachelor's degree
ECTS
3 credits
Training structure
Faculty of Science
Thermodynamic and kinetic bases to understand the optimal conditions for catalytic reactions and the requirement of activity and accessibility of catalysts.
Methods for the preparation of porous and dispersed catalysts by nucleation-growth, aggregation, and templating mechanisms.
Correlations between structural properties and activity of heterogeneous catalysts.
Examples of applications of heterogeneous catalysts to processes of refining and industrial chemistry.
Further on, basic concepts of photocatalysis and electrocatalysis are explored.
Hourly volumes:
CM: 5 p.m .
Tutorial: 8 hours
Quantum Mechanics and Modeling I
Level of education
Bachelor's degree
ECTS
5 credits
Training structure
Faculty of Science
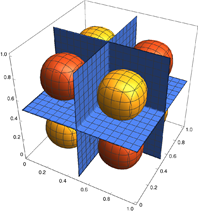
Wavefunction of an excited electron trapped in a cubic box: model for a quantum dot state
- Introduction to basic concepts in quantum physics and its relation to chemistry, modern materials science, and engineering of nanodevices.
- To achieve the goals of this course, a mathematically-rigorous approach is combined with the physical interpretation of the concepts, and the application of the most important QM models to electronic and magnetic spectroscopies and chemistry is illustrated.
Hourly volumes:
CM (Readings):24 hours
Tutorials: 12 hours
Metallurgy and electronics properties
Level of education
Bachelor's degree
ECTS
5 credits
Training structure
Faculty of Science
This teaching unit is devoted to providing an introduction to the electronic properties in the solid state of bulk and/or nanomaterials, magnetic properties in transition metal oxides, etc. This unit is taught by different external teachers alternating with UM, and the topics may vary depending on the respective area of expertise of the teaching staff.
Students should become familiar not only with the electronic properties and ordering of materials, but also with ionic and mixed electronic ionic conductors, and materials for spintronics. Another aspect concerns their specific characterizations using neutron/synchrotron diffraction as well as complementary macroscopic characterization methods for magnetism, permeability, etc.
Hourly volumes:
CM: 30 hours
TD: 3 p.m.
Research internship
Level of education
Bachelor's degree
ECTS
10 credits
Training structure
Faculty of Science
This module is devoted to an internship of at least three months in a research laboratory or industry.
Project internship
Level of education
Bachelor's degree
ECTS
3 credits
Training structure
Faculty of Science
Preparation of the 3-month research internship, exploring the state of the art of the project, preparing optimal experimental conditions, and presenting it in front of a jury.
Quantum Mechanics and Modeling II
Level of education
Bachelor's degree
ECTS
7 credits
Training structure
Faculty of Science
This course provides a complete description of the structural, electronic, and vibrational properties of molecules, together with the quantum treatment of these properties in computer simulations.
In parallel, the structural and electronic properties of solids are addressed, with an emphasis on the properties of metals and semiconductors.
Hourly volumes:
CM: 42 hours
TD: 9 p.m.
Crystallography, crystal chemistry, large-scale facilities
Level of education
Bachelor's degree
ECTS
5 credits
Training structure
Faculty of Science


This lecture is the continuation of the crystallography lecture of the1st semester and will give an advanced insight into structural characterization and structure refinements. It involves classical X-ray laboratory data collection and analysis, completed by synchrotron and neutron diffraction data analysis (powder and single crystal). The goal is to become familiar with the general principles of structure analysis, taking advantage of the complementarity of X-ray and neutron diffraction. The lecture provides detailed knowledge on how to understand and analyze phase transitions and how to deal with respective changes in the metric and associated data and structural transformations.
This lecture covers the following topics:
- Symmetry and space groups
- Introduction to structure refinement (single crystal and powder methods)
- Neutron and synchrotron facilities
- Magnetic structures with neutron diffraction
- Structure determination from single crystals (experiment and theory)
- Structure determination from powder diffraction data (experiment and theory)
- Applications of Fourier series for structure solution and refinements: from the Patterson Method to difference Fourier analysis
- Crystal twinning,
- Phase transitions
- Anomalous scattering and absolute structure determination
Hourly volumes:
CM: 30
TD: 15


