Training structure
Faculty of Science
Program
Electron Microscopy, Crystallography
6 creditsSurface properties M2
3 creditsThermodynamics and defects of solids M2
5 creditsSummer School: Large-Scale Facilities
7 credits72hProject preparation Master's Thesis
3 creditsThin films and extreme conditions M2
3 creditsMaterials for catalysis M2
3 credits
Master's thesis
30 credits
Electron Microscopy, Crystallography
Level of education
Master's degree
ECTS
6 credits
Training structure
Faculty of Science
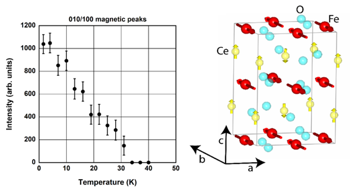
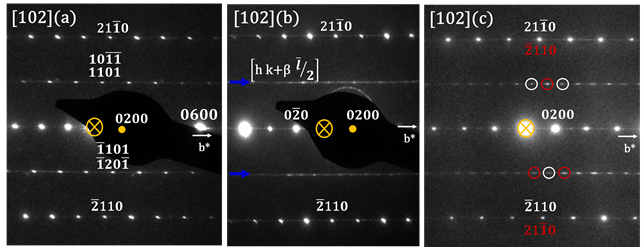
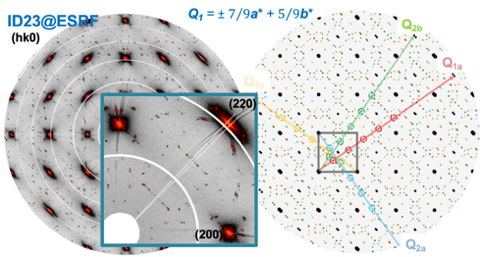
The structural characterization of materials is a mandatory prerequisite for developing functional materials and an absolute must for materials science researchers and engineers. For the interpretation of diffraction patterns, structures, microstructures, etc., detailed knowledge of crystallography, structure analysis, and the instruments used is necessary. The necessary knowledge is developed from scratch, progressively yielding an understanding of how to characterize materials by standard and sophisticated diffraction methods. The lecture also includes lab work on powder and single crystal diffractometers, allowing students to acquire the skills to correctly use and interpret diffraction data. The lecture during thefirst semester essentially covers X-ray diffraction and electron microscopy, while the crystallography part continues during thesecond semester with symmetry, structure solution, and structure refinements, as well as neutron scattering and magnetic structure analysis.
This lecture consists of two parts:
(1): Crystallography:
This part is essentially dedicated to familiarizing students with structure analysis and its application. After a brief introduction to the reciprocal lattice concept and the use of space groups in crystallography, the lecture focuses on structure analysis by diffraction methods using powder and single crystal X-ray and neutron scattering methods. This involves understanding related techniques, i.e. the use of powder and single crystal diffractometers, as well as the techniques and programs used today for structure refinements. The concept of the lecture is to introduce a basic understanding of what is behind the programs, rather than to use them blindly. Students will also collect single crystal diffraction data on a high-performance 4-cycle diffractometer with a 2D area detector, as well as magnetic structure analysis using neutron diffraction methods.
Simple inorganic structures: Space groups, X-ray/neutron and synchrotron sources, interaction of X-rays, electrons and neutrons with matter, reciprocal lattice, concept of Ewald sphere, powder diffractometers, single crystal diffractometers, orienting matrix, Patterson method, structure refinement from powder or single crystal data, magnetic structure analysis, magnetic space groups,
(2): Electron microscopy:
In this part, we will be interested in electron microscopy through flipped classes. We will discuss the following topics: Electron sources, lenses and aberrations, sample preparation, electron diffraction, structural and chemical analysis, imaging techniques.
Hourly volumes:
CM: 33 hours
Tutorial: 6 p.m.
Surface properties M2
Level of education
Master's degree
ECTS
3 credits
Training structure
Faculty of Science
This course provides comprehensive knowledge and tools related to surface properties and interfacial behavior of crystalline and amorphous solids in different media. It consists of two parts: (1) Fundamentals of Colloid and Surface Science, divided and porous solids
(2) Surface characterization techniques and surface analysis
Hourly volumes:
CM: 5 p.m .
Tutorial: 8 hours
Thermodynamics and defects of solids M2
ECTS
5 credits
Training structure
Faculty of Science
Summer School: Large-Scale Facilities
Level of education
Master's degree
ECTS
7 credits
Training structure
Faculty of Science
Hours per week
72h
The objective is to provide second-year students with a solid introduction to the use of large-scale facilities for the study and characterization of materials. In particular, we focus on the use of neutron scattering and third-generation synchrotron sources for the study of materials. Indeed, to date, the development and optimization of materials often require sophisticated methods, sometimes accessible only at large-scale facilities. This presents a major challenge for basic and applied research. The courses, which take place over two consecutive weeks, provide basic instruction on the production of neutrons and synchrotron radiation, as well as their specific applications and complementarity. The course content is as follows:
- Neutron and synchrotron sources
- Interaction of neutrons/synchrotron radiation with matter
- Diffraction methods and instrumentation for neutron and X-ray (synchrotron) scattering
- Spectroscopy: inelastic neutron scattering and X-ray absorption spectroscopy
- Magnetic neutron scattering
- Presentation of neutron and synchrotron beamlines
Project preparation Master's Thesis
Level of education
Bachelor's degree
ECTS
3 credits
Training structure
Faculty of Science
The aim of this module is to prepare the master's thesis project, which will last six months during S4.
The thesis project involves the use of large-scale facilities (preparation and obtaining access to beam time for neutron/synchrotron radiation). You will have to explore the state of the art of the master's thesis project and prepare optimal experimental conditions (optimization of experiments on light lines or neutrons).
This module will help to develop 'transversal' skills such as the development and organization of a scientific project (organization between universities and different EU research centers).
as well as communication skills.
Thin films and extreme conditions M2
ECTS
3 credits
Training structure
Faculty of Science
Materials for catalysis M2
Level of education
Master's degree
ECTS
3 credits
Training structure
Faculty of Science
Thermodynamic and kinetic bases to understand the optimal conditions for catalytic reactions and the requirement of activity and accessibility of catalysts.
Methods for the preparation of porous and dispersed catalysts by nucleation-growth, aggregation, and templating mechanisms.
Correlations between structural properties and activity of heterogeneous catalysts.
Examples of applications of heterogeneous catalysts to processes of refining and industrial chemistry.
Further on, basic concepts of photocatalysis and electrocatalysis are explored.
Hourly volumes:
CM: 5 p.m .
Tutorial: 8 hours
Master's thesis
Level of education
Master's degree
ECTS
30 credits
Training structure
Faculty of Science
Thefourth semester of the Master's program is entirely dedicated to the five-month (minimum) Master's thesis project in Materials Science. Students enroll in a research topic and contribute to a scientific problem within a research team. This allows them to apply acquired scientific skills and learn new ones in order to identify the problem and proceed toward a (possible) solution. The topic is analyzed and described in the written Master's thesis and presented orally in front of a jury. It should allow the candidate to demonstrate their ability to conduct scientific research and present it in an analytical manner.


