Training structure
Faculty of Science
Presentation
In the Chemical Sciences of Matter (SCM) program, a contemporary approach will enable students to discover materials and understand their importance in major current issues (energy, water and agri-food, health, etc.). This program is intended for students who wish to acquire scientific knowledge and skills in both the synthesis and understanding of material properties. This year (L3) of progressive specialization will enable students to apply theoretical and experimental knowledge in the field of materials chemistry, combining scientific and technological approaches.
The SCM program begins in semester 5 and continues into semester 6 of the Bachelor's degree in Chemistry, allowing students to gradually specialize in certain areas of chemistry (materials, physical chemistry, etc.), which will then be developed further at the Master's level.
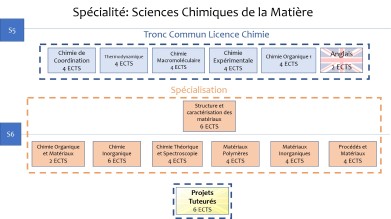
The core curriculum consists of 50% of courses that are common to all chemistry bachelor's degree programs.
Semester 5 (S5) covers the fundamentals of chemistry with courses in thermodynamics, coordination chemistry, organic chemistry, and macromolecular chemistry. Specialization begins with a dedicated course on the structure and properties of materials, which includes lectures, tutorials, and practical work allowing students to apply the knowledge they have acquired in a concrete way. S5 is based on significant experimental training in terms of knowledge and skills, with 20% of teaching devoted to practical work covering synthesis methods (microwave synthesis, hydrothermal synthesis, mechanosynthesis, etc.) and advanced analysis techniques (X-ray diffraction, scanning and energy analysis, X-ray fluorescence, thermal analysis, etc.) available at the Balard teaching hall. This hall gives students access to high-level equipment similar to that found in industry or research laboratories. Finally, a course in English, an essential language in the scientific world, whether industrial or academic, is also offered to improve language skills.
In semester 6 (S6), the program specializes further in organic, polymer, and inorganic materials, while including the theoretical foundations necessary for understanding their properties and bridging the gap to industry by including specific processes. The distinctive feature of this semester is the implementation of a supervised project in which students develop a research project under the guidance of department faculty to develop new materials or new syntheses. To this end, they have access to the teaching hall for several days, where they can use state-of-the-art equipment to carry out their project with a high degree of autonomy.
Open course in Health Access (L.AS).
Objectives
Materials are at the heart of the major societal challenges facing us in the 21st century (energy, climate change, health, water, the environment, etc.) and the SCM program will provide students with a foundation of theoretical and practical knowledge and skills in both science and technology related to materials science, which can be reused either for immediate professional integration or for further study in a master's program or engineering school.
Know-how and skills
- Master synthesis methods (inorganic chemistry/mineral chemistry/solid-state chemistry/polymers).
- Understand the structure of matter.
- Ability to observe and interpret physical and chemical behaviors (corrosion, stability, adsorption, catalysis, etc.).
- Know how to choose the characterization techniques (spectroscopic analyses, thermal analyses, electron microscopy, X-ray diffraction, etc.) suited to the synthesized materials or the properties to be highlighted.
- Master the principles and use techniques for shaping materials (metals/alloys, ceramics, polymers, composites). - Know how to study the correlations between structures/microstructures and properties (optical, electrical, magnetic, mechanical, etc.) of materials.
- Be independent, take initiative, and know how to organize your work in the laboratory.
- Work as a team.
- Respect and know how to implement health, safety, and environmental (HSE) measures and standards.
Organization
Program
Micro and macroscopic aspects of thermodynamics
4 creditsEnglish S5
2 creditsCoordination chemistry: symmetry and reactivity
4 creditsExperimental chemistry
6 creditsOrganic chemistry
4 creditsInorganic Materials: Synthesis and Characterization Part 2
3 creditsInorganic Materials - Synthesis and Characterization Part 1
3 creditsMacromolecular chemistry
4 credits
Inorganic materials: structure and properties
4 creditsProcesses and materials
4 creditsTheoretical foundations in spectroscopy
4 creditsOrganic chemistry
2 creditsSupervised projects
6 creditsPolymer materials
4 creditsAdvanced coordination chemistry
6 credits
Admission
Admission requirements
Applications can be submitted on the following platforms:
- French and European students: follow the procedure on the University of Montpellier's e-candidat website.
- International students from outside the EU: follow the " Études en France " procedure
Target audience
Students in their second year of chemistry or physics-chemistry, from IUT chemistry and preparatory classes (PCSI, TPC, etc.)
Mandatory prerequisites
Second year of chemistry or physical chemistry or technical college chemistry program or preparatory class
Recommended prerequisites
Second year of chemistry or physical chemistry or technical college chemistry program or preparatory class
And after
Continuing education
The SCM program is particularly well suited for continuing on to a master's degree in chemistry in areas such as materials, theory, separative chemistry, etc., or to a master's degree in energy, whether at the University of Montpellier or other French or foreign universities. The SCM program also allows students to enter other fields of chemistry, physical chemistry, teaching (MEEF), as well as engineering schools through competitive entrance exams. In addition, obtaining a bachelor's degree in chemistry also allows students to take civil service exams corresponding to this level of study, particularly in technical fields (forensic science, police, firefighting, etc.).
Continuing studies abroad
The quality of education in Montpellier is internationally recognized, so students on this program can consider continuing their studies with a master's degree at a foreign university. There are numerous exchange agreements between the University of Montpellier and foreign universities.
Students on the program will also have the opportunity to continue their studies in a European master's degree program, such as the MaMaSelf master's degree (Master in Materials Science Exploring Large Scale Facilities), part of which is taught in Montpellier, or the mesc+ master's degree (Materials for Energy Storage and Conversion).
Gateways and reorientation
Specialization is very important in obtaining a degree because it will determine the limits of students' areas of knowledge and skills. However, the fact that it only comes at the end of the Bachelor's degree (beginning in S5 with a lot of common ground with the other courses, before really taking effect in S6) allows students to bounce back from their L2 in general chemistry if they want to change direction at the end of the year. In this case, it will then be possible to join one of the other two chemistry bachelor's degree programs at the University of Montpellier (DNO or SCV) for one year only.
The foundation of knowledge and skills in materials chemistry could enable students who do not wish to pursue a master's degree to apply for one of the many professional bachelor's degrees in the field of chemistry in order to enroll in a work-study program, for example. A reorientation toward L3pro (L3pro couleur de Montpellier, for example) is thus possible with direct integration into the professional world upon graduation.
Professional integration
Upon completion of the university program (Master's/PhD), the training in materials chemistry provides excellent career prospects in positions directly related to the skills acquired and with commensurate remuneration. Students who have specialized in Materials Chemistry are highly sought after in industry (engineering and design offices, R&D engineering, etc.) as well as in teaching and academic research. The placement rate for students in Montpellier who have completed a Master's degree in Chemistry is over 80% within three months of graduation.